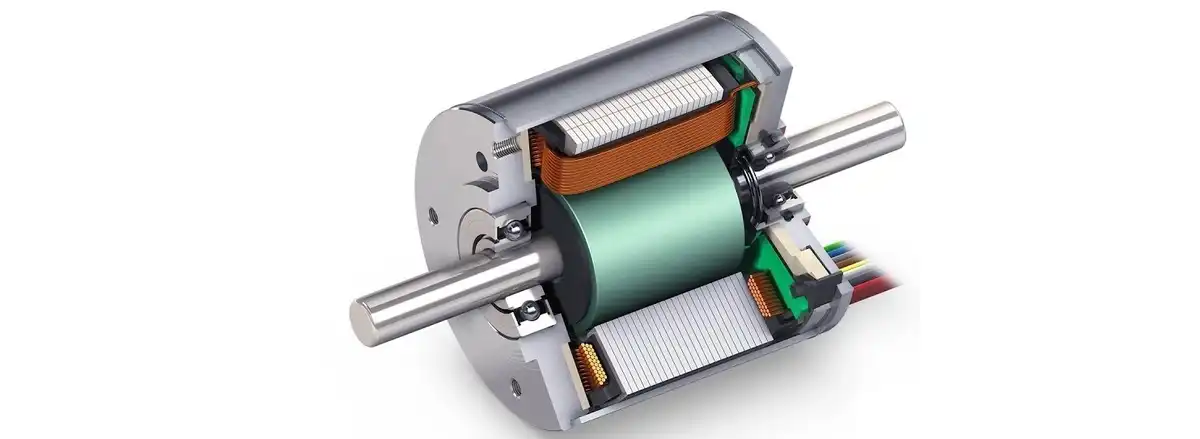

There are two main mechanisms that make up a DC motor: the stator and the rotor. The annular iron core together with the supporting windings and coils form the rotor. The rotation of the iron core in the magnetic field causes the coils to generate voltage, thereby generating eddy currents. Eddy current is a magnetic loss, when a DC motor loses power due to eddy current flow, it is called eddy current loss.
Various factors affect the amount of power loss due to eddy current flow, including the thickness of the magnetic material, the frequency of the induced electromotive force, and the density of the magnetic flux. The electrical resistance of the material flowing through the current affects how eddy currents form. For example, as the cross-sectional area of the metal decreases, this results in a decrease in eddy currents. Therefore, the material must be kept thinner to minimize the cross-sectional area to reduce the amount of eddy currents and losses.
The reduction of eddy current is the main reason for the use of several thin iron sheets or sheets in the armature core, thinner sheets are used to create a higher resistance, resulting in less eddy currents, which ensures that more eddy current losses occur. Small, each individual piece of iron is called a lamination. The material of the motor lamination is electrical steel, silicon steel, also called electrical steel, which is steel added with silicon. Adding silicon can ease the penetration of the magnetic field, increase its resistance, and reduce the hysteresis loss of the steel. Silicon steel is essential for electromagnetic fields. Less electrical applications such as motor stators/rotors and transformers.
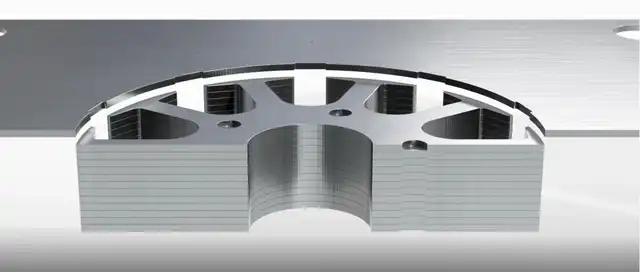
The silicon in silicon steel helps reduce corrosion, but the main reason for adding silicon is to reduce the steel's hysteresis, which is the time delay between when a magnetic field is first created or attached to the steel and the magnetic field. The added silicon makes the steel more efficient and faster to generate and maintain magnetic fields, which means that silicon steel increases the efficiency of any device that uses steel as a magnetic core material. Metal stamping is a process for producing motor laminations for different applications. Metal stamping can provide customers with a wide range of customization capabilities, and molds and materials can be designed according to customer specifications.
Motor stamping is a type of metal stamping that was first used in mass-produced bicycles in the 1880s. Stamping replaced part production with die forging and machining, which significantly reduced part cost. Although stamped parts are not as strong as die forgings, they are of sufficient quality for mass production.
The import of stamped bicycle parts from germany into the united states began in 1890, and american companies subsequently began to have stamping machines custom-made by american machine tool builders, and several automakers began using stamped parts before the ford motor company.
Metal stamping is a cold forming process that uses dies and punches to punch sheet metal into different shapes. A flat sheet of metal, often called a blank, is fed into a punch, which uses tools or dies to transform the metal into new shapes. Shape. The material to be punched is placed between die sections, where pressure is used to shape and cut the material into the final form required for the product or component.
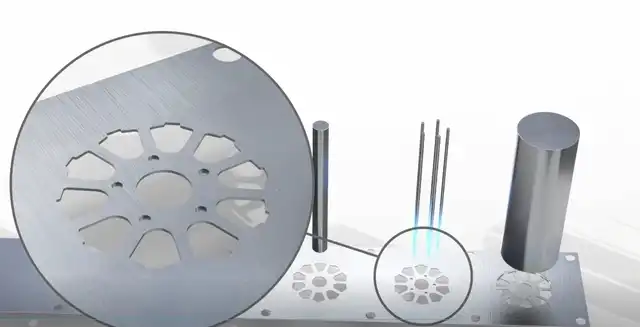
Each station in the tool performs a different cut, punch, or bend as the metal strip passes through the progressive punch, unrolling smoothly from the coil, and the process of each successive station adds to the work of the previous station. , thus forming a complete part. There are some upfront costs involved in investing in permanent steel dies, but significant savings can be achieved by increasing efficiency and production speed, as well as combining multiple forming operations into a single machine. Strong resistance to impact and abrasive forces.
Stamping, also known as pressing, can be performed in conjunction with other metal forming processes and can consist of one or more of a range of more specific processes or techniques such as stamping, blanking, embossing, embossing, bending, flanged and laminated.
A die is used to cut metal into different shapes, and punching is when a punch enters the die to remove a piece of scrap, leaving a hole in the workpiece. Blanking, on the other hand, removes the workpiece from the main material and the removed metal part is a new workpiece or blank.
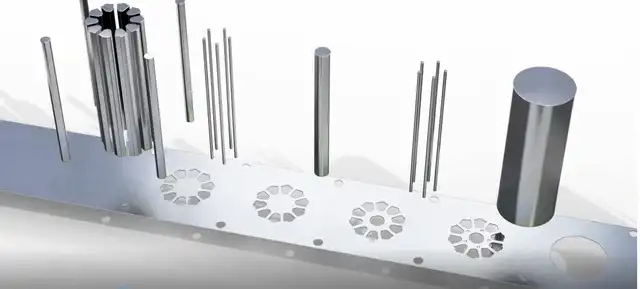
Embossing creates raised or recessed designs in sheet metal by pressing the blank onto a die containing the desired shape, or by feeding a blank of material into a roll die. Stamping is a bending technique in which a workpiece is punched by placing it between a die and a punch or press, a series of actions that cause the tip of the punch to pierce the metal and create a new shape. Bending is a way of forming metal into a desired shape, such as an l, u, or v profile, and bending usually occurs around a single axis. Flanging is the process of introducing a flare or flange into a metal workpiece by using a die, press or specialized flanging machinery.
Metal stamping machines don’t just punch, they cast, cut, stamp and form sheet metal, and machines can build highly accurate and repeatable shapes through programming or computer numerical control (CNC), electrical discharge machining (EDM) and computer-aided design (CAD) program ensures accuracy.